The concept of energy is multifaceted and can be categorized into various types, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Understanding these different forms of energy is crucial for harnessing, converting, and utilizing them efficiently in our daily lives and technological advancements. The seven primary types of energy are kinetic, potential, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, and renewable energy, with some sources also categorizing radiant (light) energy as a distinct form. Each of these types plays a significant role in the global energy landscape, contributing to how we generate power, fuel our vehicles, heat our homes, and power our devices.
Introduction to Primary Energy Types
Energy is the driving force behind all physical phenomena, enabling us to perform work, whether it’s moving an object from one place to another, heating water, or powering a computer. The primary types of energy are fundamental because they cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another, as stated by the law of conservation of energy. This principle underlines the versatility and interconvertibility of energy forms, which is pivotal for energy production, storage, and consumption.
Kinetic and Potential Energy
Kinetic energy is associated with motion; any moving object possesses kinetic energy. The amount of kinetic energy an object has depends on its mass and the square of its velocity. On the other hand, potential energy is the energy an object has due to its position or configuration. For example, water stored behind a dam has potential energy due to its height, which can be converted into kinetic energy when released. Both kinetic and potential energy are forms of mechanical energy and are crucial in understanding how machines and engines work.
| Type of Energy | Description |
|---|---|
| Kinetic Energy | Energy of motion |
| Potential Energy | Energy due to position or configuration |
Thermal, Electrical, and Chemical Energy

Thermal energy is the energy an object has due to the motion of its particles, which is a function of its temperature. Electrical energy is the energy caused by the movement of electrons. It powers most of our electronic devices and is a critical form of energy for modern civilization. Chemical energy, stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules, is released during chemical reactions, such as combustion. This form of energy is the basis for fossil fuel combustion, which generates a significant portion of the world’s electricity and powers vehicles.
Nuclear and Renewable Energy
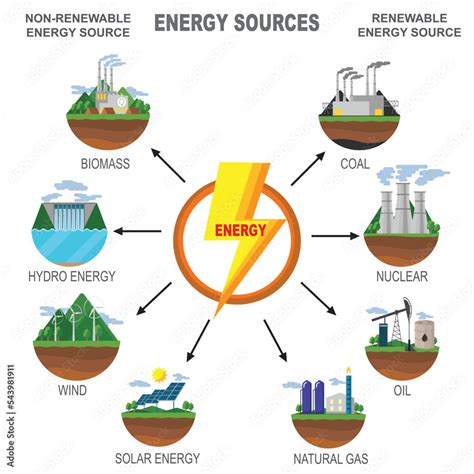
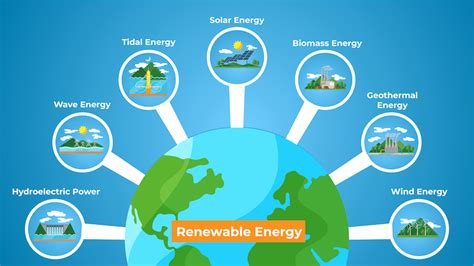
Nuclear energy is released during nuclear reactions, either fission (splitting heavy atoms) or fusion (combining light atoms), and is harnessed to generate electricity in nuclear power plants. Renewable energy, on the other hand, comes from natural resources that can be replenished over time, such as sunlight, wind, rain, and geothermal heat. Renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly important as the world transitions towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy solutions to mitigate climate change and ensure energy security.
Key Points
- Kinetic and potential energy are fundamental forms of mechanical energy.
- Thermal, electrical, and chemical energies are crucial for technological applications and daily life.
- Nuclear energy provides a significant portion of the world's electricity.
- Renewable energy sources are vital for sustainable development and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy conversion and efficiency are key factors in harnessing and utilizing energy effectively.
The diversity of energy types reflects the complexity and richness of the natural world, offering numerous paths for innovation and progress. As our understanding of energy and its applications evolves, so does our capacity to harness, convert, and utilize it in ways that are more efficient, sustainable, and beneficial to humanity and the planet.
What is the most abundant form of energy on Earth?
+Solar energy, a form of renewable energy, is the most abundant form of energy available on Earth, as the sun's rays cover the entire planet, making it a virtually unlimited resource.
How is nuclear energy harnessed?
+Nuclear energy is harnessed through nuclear reactions, primarily nuclear fission, in reactors designed to control and sustain these reactions, producing steam that drives turbines to generate electricity.
What is the role of energy efficiency in sustainable development?
+Energy efficiency plays a critical role in sustainable development by reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services, thereby decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and the environmental impact of energy production and consumption.
In conclusion, the seven types of energy form the backbone of our energy landscape, each with its unique characteristics, applications, and potential for innovation. As we navigate the challenges of the 21st century, understanding and effectively utilizing these energy forms will be pivotal in creating a more sustainable, efficient, and prosperous world for future generations.