As the world shifts towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious approach to energy consumption, home power energy systems have become an increasingly popular choice for homeowners looking to reduce their reliance on the grid and lower their energy bills. With the cost of renewable energy technologies like solar and wind power decreasing dramatically in recent years, it's now more feasible than ever for individuals to generate their own clean energy and achieve energy independence. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the world of home power energy systems, exploring the different types of systems available, their benefits and drawbacks, and what you need to know to get started on your own energy self-sufficiency journey.
Key Points
- Home power energy systems can significantly reduce energy bills and carbon footprint
- Solar, wind, and hydro power are the most common types of renewable energy systems for homes
- Energy storage systems like batteries are crucial for maintaining a stable power supply
- Net metering and grid tie systems allow homeowners to sell excess energy back to the grid
- Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential for optimal system performance
Types of Home Power Energy Systems

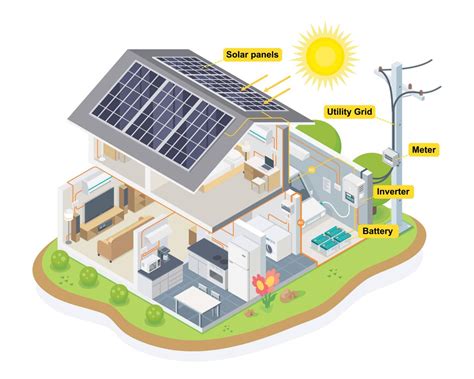
There are several types of home power energy systems to choose from, each with its own unique characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks. The most common types of systems include solar power, wind power, and hydro power. Solar power systems, for example, use photovoltaic (PV) panels to convert sunlight into electricity, while wind power systems use turbines to generate electricity from wind energy. Hydro power systems, on the other hand, harness the energy of moving water to generate electricity. When choosing a home power energy system, it’s essential to consider factors like climate, geography, and energy needs to determine the most suitable option.
Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems are one of the most popular types of home power energy systems, and for good reason. They’re relatively low maintenance, easy to install, and can be highly efficient. A typical solar power system consists of PV panels, an inverter, a mounting system, and a monitoring system. The PV panels convert sunlight into DC power, which is then converted into AC power by the inverter and fed into the home’s electrical panel. With the cost of solar panels decreasing dramatically in recent years, solar power systems have become an increasingly affordable option for homeowners.
| System Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Photovoltaic (PV) Panels | Convert sunlight into DC power |
| Inverter | Convert DC power into AC power |
| Mounting System | Secures PV panels to the roof or ground |
| Monitoring System | Tracks system performance and energy production |

Wind Power Systems
Wind power systems are another popular type of home power energy system, particularly in areas with strong and consistent winds. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electricity, which is then fed into the home’s electrical panel. While wind power systems can be highly efficient, they do require more maintenance than solar power systems and can be noisy. However, for homeowners with the right location and wind conditions, wind power systems can be a highly effective way to generate clean energy.
Energy Storage Systems

Energy storage systems are a crucial component of any home power energy system, as they allow homeowners to store excess energy generated by their system for later use. This is particularly important for systems like solar and wind power, which can be intermittent and unpredictable. Energy storage systems like batteries can help to stabilize the power supply, providing a backup source of energy during periods of low energy production. When choosing an energy storage system, it’s essential to consider factors like capacity, depth of discharge, and cycle life to determine the most suitable option.
Net Metering and Grid Tie Systems
Net metering and grid tie systems allow homeowners to sell excess energy generated by their home power energy system back to the grid. This can be a highly beneficial arrangement, as it enables homeowners to offset their energy bills and even generate revenue. Net metering systems measure the amount of energy produced by the home power energy system and subtract it from the amount of energy consumed by the home. Grid tie systems, on the other hand, allow homeowners to feed excess energy back into the grid, where it can be used by other consumers.
In conclusion, home power energy systems offer a highly effective way for homeowners to reduce their reliance on the grid, lower their energy bills, and achieve energy independence. With the cost of renewable energy technologies decreasing dramatically in recent years, it's now more feasible than ever for individuals to generate their own clean energy. By understanding the different types of home power energy systems available, their benefits and drawbacks, and what you need to know to get started, you can make an informed decision about which system is right for you.
What is the average cost of a home power energy system?
+The average cost of a home power energy system can vary widely, depending on the type and size of the system. However, the cost of solar power systems, for example, has decreased dramatically in recent years, with the average cost of a solar panel system ranging from 15,000 to 30,000.
How long does it take to install a home power energy system?
+The installation time for a home power energy system can vary depending on the complexity of the system and the size of the installation team. However, a typical solar power system installation can take anywhere from a few days to a week to complete.
What are the benefits of using a home power energy system?
+The benefits of using a home power energy system are numerous, including reduced energy bills, increased energy independence, and a lower carbon footprint. Home power energy systems can also increase property values and provide a sense of security and self-sufficiency.