Hydroelectric power, one of the oldest and largest sources of renewable energy, has been a cornerstone of electricity generation for over a century. However, despite its potential, a significant amount of hydroelectric power is wasted due to various inefficiencies in the system. This wasted energy not only represents a loss of valuable resources but also contributes to the overall inefficiency of the power generation and distribution process. Understanding the reasons behind this wasted energy and exploring ways to mitigate these losses is crucial for maximizing the benefits of hydroelectric power and ensuring a more sustainable energy future.
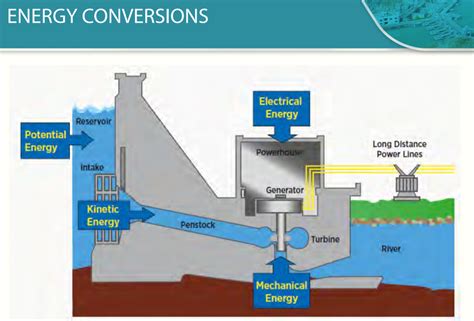
The hydroelectric power process involves the conversion of the kinetic energy of moving water into electrical energy. This is achieved through the use of turbines, which are driven by the flow of water from a higher elevation to a lower elevation, typically from a dam. The rotation of the turbines is then converted into electrical energy by generators. While the principle of hydroelectric power generation is straightforward, the actual process is complex and involves various stages where energy can be lost. These losses can occur due to mechanical inefficiencies in the turbines and generators, transmission losses as the electricity is conveyed from the power plant to the consumer, and even due to the evaporation of water from the reservoirs, which reduces the amount of water available for power generation.
Key Points
- Hydroelectric power generation is affected by inefficiencies leading to wasted energy.
- Mechanical losses in turbines and generators, transmission losses, and reservoir evaporation are primary causes of energy waste.
- Improving turbine efficiency, enhancing transmission infrastructure, and implementing water conservation measures can help mitigate these losses.
- Advancements in technology, such as pumped storage hydroelectricity and run-of-river systems, offer potential for increased efficiency and reduced waste.
- Policy and regulatory support are essential for promoting the development and optimization of hydroelectric power resources.
Causes of Wasted Energy in Hydroelectric Power

The causes of wasted energy in hydroelectric power systems are multifaceted and can be broadly categorized into technical, operational, and environmental factors. Technically, the efficiency of turbines and generators plays a significant role. Older power plants may have outdated technology with lower efficiency rates compared to modern plants. Moreover, the transmission of electricity over long distances results in energy losses due to resistance in the transmission lines. Operationally, the management of water flow and reservoir levels can significantly impact the efficiency of hydroelectric power generation. For instance, maintaining optimal water levels and flow rates is crucial for maximizing turbine efficiency. Environmental factors, such as climate change, can alter precipitation patterns and water availability, affecting the overall potential for hydroelectric power generation.
Technical Inefficiencies
Technical inefficiencies in hydroelectric power systems are primarily related to the conversion process of kinetic energy into electrical energy. The turbines and generators used in hydroelectric power plants are not 100% efficient, meaning some of the energy is lost as heat or vibration. Additionally, the transmission lines that carry electricity from the power plant to the consumers also lose energy due to electrical resistance. These technical losses can be mitigated through the use of more efficient technologies, such as advanced turbine designs and high-temperature superconducting transmission lines. However, the implementation of such technologies requires significant investment and technological advancements.
| Efficiency Component | Typical Efficiency Range |
|---|---|
| Turbine Efficiency | 90% - 95% |
| Generator Efficiency | 95% - 98% |
| Transmission Efficiency | 90% - 95% |

Solutions and Future Directions

Addressing the issue of wasted energy in hydroelectric power requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses technological innovation, operational optimization, and policy support. Technological advancements, such as the development of more efficient turbines and generators, can directly improve the conversion efficiency of hydroelectric power plants. Operational strategies, including the optimization of water flow and reservoir management, can also play a crucial role in maximizing the energy output of these plants. Moreover, policy and regulatory frameworks that encourage the development and modernization of hydroelectric power infrastructure are essential for promoting efficiency and reducing waste.
One of the promising future directions for hydroelectric power is the development of pumped storage hydroelectricity (PSH) and run-of-river (ROR) systems. PSH involves pumping water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir during off-peak hours, using excess energy from other power sources, and then releasing the water to generate electricity during peak demand hours. This method can significantly increase the flexibility and efficiency of hydroelectric power generation. ROR systems, which harness the energy of rivers without the need for large reservoirs, offer another avenue for reducing environmental impacts and increasing the overall efficiency of hydroelectric power generation.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
The role of policy and regulatory frameworks in promoting the efficiency and sustainability of hydroelectric power cannot be overstated. Governments and regulatory bodies can incentivize the development and modernization of hydroelectric power infrastructure through tax credits, grants, and streamlined permitting processes. Additionally, policies that promote the integration of hydroelectric power with other renewable energy sources can help create a more resilient and efficient energy system. Public awareness and education campaigns can also play a vital role in supporting the development of hydroelectric power by addressing concerns and fostering community support for projects.
What are the primary causes of wasted energy in hydroelectric power systems?
+The primary causes include technical inefficiencies in turbines and generators, transmission losses, and operational factors such as reservoir evaporation and suboptimal water flow management.
How can the efficiency of hydroelectric power plants be improved?
+Improving turbine and generator efficiency, enhancing transmission infrastructure, optimizing operational parameters, and adopting technologies like pumped storage hydroelectricity can help improve efficiency.
What role do policy and regulatory frameworks play in promoting hydroelectric power efficiency?
+Policies and regulations can incentivize the development and modernization of hydroelectric infrastructure, promote public awareness, and support the integration of hydroelectric power with other renewable energy sources.
In conclusion, while hydroelectric power is a vital component of the global renewable energy landscape, it is not immune to inefficiencies and wasted energy. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that includes technological innovation, operational optimization, and supportive policy frameworks. By understanding the causes of wasted energy and implementing strategies to mitigate these losses, we can unlock the full potential of hydroelectric power and contribute to a more sustainable and efficient energy future.