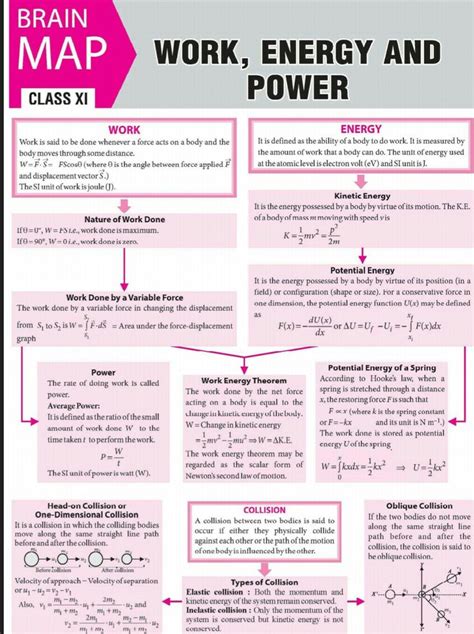
The concepts of work, energy, and power are fundamental to understanding the principles of physics. These three concepts are interrelated and are essential in describing the motion of objects and the forces that act upon them. In this article, we will delve into the world of work, energy, and power, exploring their definitions, types, and applications in the field of physics.
Introduction to Work, Energy, and Power

Work, energy, and power are three closely related concepts in physics that help us understand how objects move and respond to forces. Work is defined as the transfer of energy from one object to another through a force applied over a distance. Energy, on the other hand, is the ability of an object to do work, and it comes in various forms, such as kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, and more. Power, the third concept, is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred.
Key Points
- Work is the transfer of energy from one object to another through a force applied over a distance.
- Energy is the ability of an object to do work and comes in various forms, including kinetic, potential, thermal, and more.
- Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred.
- The unit of work and energy is the joule (J), while the unit of power is the watt (W).
- The work-energy theorem states that the net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy.
Types of Energy
Energy is a fundamental concept in physics and comes in various forms, each with its own characteristics and applications. The main types of energy include:
- Kinetic Energy: The energy of motion, which an object possesses due to its velocity.
- Potential Energy: The energy an object has due to its position or configuration, such as gravitational potential energy or elastic potential energy.
- Thermal Energy: The energy of heat, which is the kinetic energy of particles in a substance.
- Electrical Energy: The energy associated with the movement of charged particles, such as electrons.
- Chemical Energy: The energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules, which can be released through chemical reactions.
Work and Energy Theorem

The work-energy theorem is a fundamental principle in physics that relates the work done on an object to its change in kinetic energy. The theorem states that the net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy. Mathematically, this can be expressed as W = ΔKE, where W is the net work done, and ΔKE is the change in kinetic energy.
| Energy Type | Formula | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Kinetic Energy | KE = (1/2)mv^2 | Joule (J) |
| Potential Energy | PE = mgh | Joule (J) |
| Thermal Energy | Q = mcΔT | Joule (J) |

Power and Efficiency
Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. It is an important concept in physics and engineering, as it helps us understand how quickly energy is being used or produced. The unit of power is the watt (W), which is defined as one joule per second (J/s). Efficiency, on the other hand, is a measure of how well an energy conversion process is performed, and it is defined as the ratio of the output energy to the input energy.
Applications of Work, Energy, and Power
The concepts of work, energy, and power have numerous applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and technology. Some of the key applications include:
- Transportation: The principles of work, energy, and power are used in the design and optimization of vehicles, such as cars, airplanes, and bicycles.
- Energy Generation: The concepts of energy and power are used in the design and operation of power plants, including fossil fuel, nuclear, and renewable energy sources.
- Electronics: The principles of energy and power are used in the design and operation of electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, and televisions.
What is the difference between work and energy?
+Work is the transfer of energy from one object to another through a force applied over a distance, while energy is the ability of an object to do work.
What is the unit of power?
+The unit of power is the watt (W), which is defined as one joule per second (J/s).
What is the work-energy theorem?
+The work-energy theorem states that the net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy, which can be expressed mathematically as W = ΔKE.
In conclusion, the concepts of work, energy, and power are fundamental to understanding the principles of physics and have numerous applications in various fields. By grasping these concepts, we can better appreciate the workings of the physical world and develop innovative solutions to real-world problems.