Rapid advancements in technology have made renewable energy a vital component of the global energy mix, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change. The shift towards renewable energy sources is not only essential for environmental sustainability but also presents vast economic opportunities. Among the various forms of renewable energy, five primary methods have emerged as leading power generators: solar energy, wind energy, hydro energy, geothermal energy, and biomass energy. Each of these methods offers unique advantages and contributes significantly to the global transition towards cleaner, more sustainable energy production.
Key Points
- Solar energy harnesses sunlight to generate power through photovoltaic panels or solar thermal systems.
- Wind energy converts wind kinetic energy into electricity using wind turbines.
- Hydro energy generates power by leveraging the movement of water in rivers, oceans, or tidal currents.
- Geothermal energy utilizes the heat from the Earth's core to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity.
- Biomass energy involves burning organic materials to produce electricity or heat.
Solar Energy: Harnessing Sunlight for Power
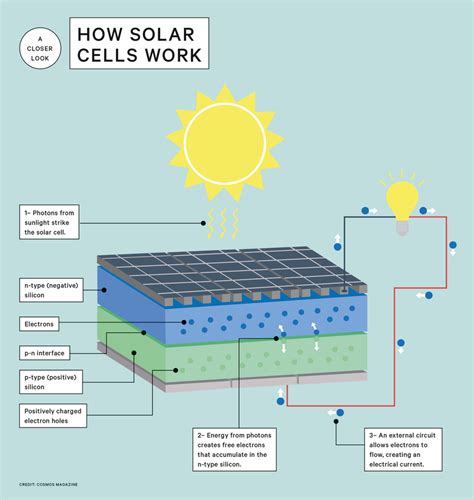
Solar energy is one of the most promising renewable energy sources, given its abundance and the advancements in solar panel technology. There are two primary methods of generating power from sunlight: photovoltaic (PV) systems and solar thermal systems. Photovoltaic systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconducting materials, while solar thermal systems use sunlight to heat water or a fluid, which then generates electricity through a steam turbine. As of 2022, the global solar PV capacity reached approximately 843 gigawatts (GW), with countries like China, the United States, and Japan leading in solar energy production.
Advancements in Solar Panel Efficiency
Recent years have seen significant improvements in solar panel efficiency, with the development of bifacial panels and perovskite solar cells offering higher power conversion efficiency rates. Bifacial solar panels can generate electricity from both the front and back sides of the panel, increasing energy output by up to 25%. Perovskite solar cells, on the other hand, have shown power conversion efficiency rates of over 23%, outperforming traditional silicon-based solar cells. These advancements are crucial for making solar energy more competitive with fossil fuels and for accelerating its adoption worldwide.
Wind Energy: Converting Wind into Electricity

Wind energy is another vital source of renewable energy, with wind turbines converting the kinetic energy in the wind into electrical power. The global wind power market has experienced substantial growth, with total installed capacity exceeding 740 GW by the end of 2022. Wind energy is particularly appealing for countries with extensive coastlines or open plains, where wind speeds are consistently high. Technological innovations, such as larger turbines and advanced blade designs, have increased the efficiency and reduced the costs of wind energy production.
Offshore Wind Farms: The Future of Wind Energy
Offshore wind farms have emerged as a significant sector within the wind energy industry, offering stronger and more consistent winds compared to onshore locations. The development of larger turbines and floating wind technologies has made it possible to harness wind energy in deeper waters, further from the coast. This not only reduces visual impact but also allows for the exploitation of more powerful and reliable wind resources. Countries like the United Kingdom, Denmark, and China are leading in offshore wind energy, with ambitious plans to expand their capacities in the coming years.
Hydro Energy: Power from Moving Water
Hydro energy, or hydropower, is the oldest and largest source of renewable energy, accounting for over 60% of the world’s renewable electricity generation. Hydroelectric power plants generate electricity by channeling water from a dam or river through turbines. The potential for hydro energy is vast, especially in regions with significant water resources. However, the development of new hydroelectric projects faces challenges related to environmental impact, social displacement, and high upfront costs.
Tidal and Wave Energy: The Untapped Potential
Beyond traditional hydropower, tidal and wave energy represent untapped potential for renewable energy generation. Tidal barrages and stream generators can harness the predictable and reliable energy from tidal currents, while wave energy converters can capture the kinetic energy in ocean waves. These technologies are still in the early stages of development but offer promising opportunities for coastal communities and islands, where they can provide reliable and clean energy.
Geothermal Energy: Leveraging Earth’s Heat
Geothermal energy utilizes the heat from the Earth’s core to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. This form of energy is particularly suitable for regions with significant volcanic activity, such as Iceland, Indonesia, and the Philippines. Geothermal power plants can operate at a capacity factor of 90% or more, making them one of the most reliable sources of renewable energy. However, the high exploration and development costs, along with the limited geographical suitability, restrict the widespread adoption of geothermal energy.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS): Expanding Geothermal Potential
Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) are engineered reservoirs that can be created in hot rock formations without natural permeability, potentially expanding the reach of geothermal energy beyond traditional volcanic areas. EGS technology involves drilling into hot rock, fracturing the rock to increase its permeability, and then circulating water through the system to generate steam. This approach could unlock geothermal resources in a wider range of locations, making geothermal energy a more viable option for a larger number of countries and communities.
Biomass Energy: Power from Organic Materials

Biomass energy involves burning organic materials such as wood, crops, and waste to produce electricity or heat. It is a versatile energy source that can be used for power generation, heating, and as a transportation fuel. Biomass can be converted into energy through various processes, including combustion, anaerobic digestion, and gasification. However, the sustainability of biomass energy depends on the source of the biomass and the efficiency of the conversion process. Sustainable biomass production ensures that the removal of organic materials does not harm the environment and that the biomass is replenished at a rate equal to or greater than the rate of removal.
Sustainable Biomass Production: Balancing Energy Needs with Environmental Concerns
The key to sustainable biomass production lies in managing land use, ensuring that biomass feedstocks are produced with minimal environmental impact, and maximizing the energy output per unit of biomass input. This can be achieved through efficient agricultural practices, the use of waste biomass, and the implementation of certification schemes that verify the sustainability of biomass production. As technology continues to evolve, biomass energy can play a critical role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions from energy production, especially in sectors that are difficult to decarbonize, such as aviation and heavy industry.
| Renewable Energy Source | Global Capacity (2022) | Growth Rate (2020-2022) |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Energy | 843 GW | 20% |
| Wind Energy | 740 GW | 15% |
| Hydro Energy | 1,200 GW | 5% |
| Geothermal Energy | 13 GW | 10% |
| Biomass Energy | 130 GW | 8% |
What is the most widely used form of renewable energy?
+Hydro energy is the most widely used form of renewable energy, accounting for over 60% of the world's renewable electricity generation.
How does solar energy generate power?
+Solar energy generates power through photovoltaic (PV) systems, which convert sunlight directly into electricity, and solar thermal systems, which use sunlight to heat water or a fluid to produce steam that drives turbines.
What are the advantages of offshore wind farms?
+Offshore wind farms offer stronger and more consistent winds, reducing visual impact and allowing for the exploitation of more powerful and reliable wind resources. They also enable the development of larger turbines and floating wind technologies.
How does geothermal energy work?
+Geothermal energy works by utilizing the heat from the Earth's core to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. This form of energy is particularly suitable for regions with significant volcanic activity.
What is the role of biomass energy in the renewable energy mix?
+Biomass energy plays a critical role in the renewable energy mix, especially in sectors that are difficult to decarbonize, such as aviation and heavy industry. It involves burning organic materials to produce electricity or heat and can be a versatile and sustainable energy source when produced with minimal environmental impact.
Rapid advancements in renewable energy technologies, coupled with declining costs and increasing efficiencies, are driving the global transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy systems. As the world moves forward, the integration of solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy will be essential for meeting energy demands while addressing the pressing issue of climate change. With continued innovation and investment, renewable energy can pave the way for a more sustainable future, where energy production not only powers our lives but also protects the planet for generations to come.
Meta Description: Discover the five primary ways renewable energy generates power, including solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy, and explore their roles in the global transition towards sustainable energy systems.



