The energy grid, a complex network of power plants, transmission lines, and distribution infrastructure, plays a vital role in supplying electricity to meet the growing demands of modern society. As the world transitions towards a more sustainable and renewable energy-based economy, the energy grid is undergoing a significant transformation. This shift is driven by the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve energy efficiency, and ensure a reliable supply of electricity. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the energy grid, exploring its current state, the challenges it faces, and the innovative solutions being implemented to create a more resilient and sustainable energy system.
Key Points
- The energy grid is a critical infrastructure that requires significant upgrades to accommodate the integration of renewable energy sources.
- Smart grid technologies, such as advanced sensors and IoT devices, are being deployed to enhance grid efficiency and reliability.
- Energy storage systems, including batteries and other innovative solutions, are crucial for mitigating the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
- Grid modernization efforts are focused on creating a more flexible, adaptable, and resilient energy system that can respond to changing energy demands.
- Electric vehicles and building electrification are driving increased demand for electricity, highlighting the need for a more efficient and sustainable energy grid.
Evolution of the Energy Grid
The energy grid has undergone significant changes since its inception, with the introduction of new technologies and energy sources transforming the way electricity is generated, transmitted, and distributed. The traditional grid, which relied heavily on centralized power plants and a one-way flow of electricity, is being replaced by a more decentralized and dynamic system. This shift is driven by the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, which are inherently intermittent and require a more flexible and responsive grid.
Challenges Facing the Energy Grid
Despite the progress made in modernizing the energy grid, several challenges persist, including the integration of renewable energy sources, energy storage, and grid resilience. The intermittency of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, requires advanced energy storage systems to mitigate the impact of variable energy output. Furthermore, the increasing demand for electricity, driven by electric vehicles and building electrification, is placing additional strain on the grid, highlighting the need for more efficient and sustainable energy systems.
| Energy Source | Capacity Factor | Intermittency |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Power | 25% | High |
| Wind Power | 35% | High |
| Nuclear Power | 92% | Low |
| Coal Power | 70% | Low |

Smart Grid Technologies
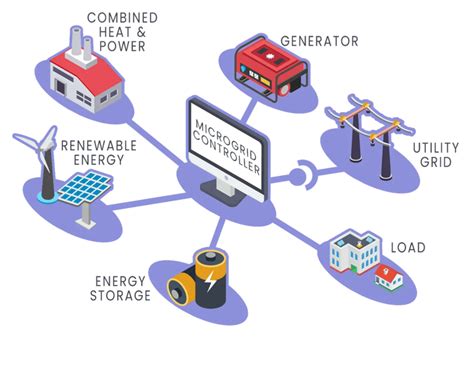
Smart grid technologies, including advanced sensors, IoT devices, and data analytics platforms, are being deployed to enhance grid efficiency, reliability, and resilience. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of the grid, allowing for more precise management of energy distribution and consumption. Furthermore, smart grid systems can integrate renewable energy sources, energy storage, and electric vehicles, creating a more dynamic and responsive energy system.
Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage systems, including batteries, pumped hydro storage, and other innovative solutions, are critical for mitigating the intermittency of renewable energy sources. These systems can store excess energy generated by renewable sources during periods of low demand, releasing it back into the grid when demand increases. This capability enables a more stable and reliable energy supply, reducing the strain on the grid and supporting the widespread adoption of renewable energy.
Grid Modernization Efforts
Grid modernization efforts are focused on creating a more flexible, adaptable, and resilient energy system that can respond to changing energy demands. This includes the deployment of advanced technologies, such as smart grid systems, energy storage, and grid management software. Furthermore, grid modernization involves the integration of renewable energy sources, electric vehicles, and building electrification, highlighting the need for a more efficient and sustainable energy grid.
What is the primary challenge facing the energy grid?
+The primary challenge facing the energy grid is the integration of renewable energy sources, which are inherently intermittent and require advanced energy storage systems to mitigate their impact on the grid.
How can smart grid technologies enhance grid efficiency and reliability?
+Smart grid technologies, including advanced sensors and IoT devices, enable real-time monitoring and control of the grid, allowing for more precise management of energy distribution and consumption.
What role do energy storage systems play in mitigating the intermittency of renewable energy sources?
+Energy storage systems, including batteries and other innovative solutions, can store excess energy generated by renewable sources during periods of low demand, releasing it back into the grid when demand increases, thereby mitigating the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
In conclusion, the energy grid is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the need to integrate renewable energy sources, improve energy efficiency, and ensure a reliable supply of electricity. By leveraging advanced technologies, such as smart grid systems and energy storage, we can create a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable energy system that meets the needs of a rapidly changing world. As the energy landscape continues to evolve, it is essential to prioritize grid modernization efforts, supporting the widespread adoption of renewable energy and creating a more sustainable future for generations to come.



