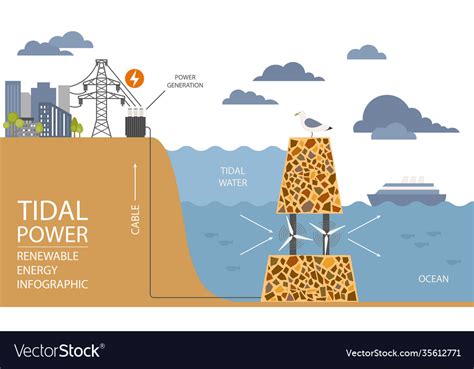
Tidal power, a form of renewable energy, harnesses the natural power of ocean tides to generate electricity. This innovative technology has the potential to provide a significant portion of the world's energy needs, particularly in coastal regions. As the world shifts towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, understanding how tidal power works is crucial. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of tidal power, exploring its fundamental principles, types of tidal power technologies, and the benefits it offers.
Key Points
- Tidal power generates electricity by harnessing the kinetic energy of ocean tides.
- There are several types of tidal power technologies, including tidal barrages, tidal stream generators, and tidal lagoons.
- Tidal power offers several benefits, including predictability, reliability, and minimal environmental impact.
- The cost of tidal power is decreasing, making it more competitive with traditional forms of energy.
- Tidal power has the potential to provide a significant portion of the world's energy needs, particularly in coastal regions.
Principles of Tidal Power

Tidal power works on the principle of harnessing the kinetic energy of ocean tides. Tides are the periodic rising and falling of the sea level caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun. As the tide rises, water flows into a specific area, creating a current. This current can be harnessed using various technologies to generate electricity. The process involves converting the kinetic energy of the tidal current into electrical energy, which can then be transmitted to the power grid and distributed to homes and businesses.
Tidal Barrages
One of the most common types of tidal power technologies is the tidal barrage. A tidal barrage is a dam-like structure built across a tidal estuary. As the tide rises, water flows into the barrage, creating a reservoir of water. As the tide falls, the water is released back into the sea, passing through turbines, which generate electricity. Tidal barrages are typically used in areas with high tidal ranges, such as the Bay of Fundy in Canada, where the tidal range can reach up to 16 meters.
| Tidal Barrage Location | Tidal Range | Installed Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Bay of Fundy, Canada | 16 meters | 1,400 MW |
| La Rance, France | 13 meters | 240 MW |
| Severn Estuary, UK | 15 meters | 8,640 MW |

Tidal Stream Generators

Tidal stream generators are another type of tidal power technology. These devices are similar to wind turbines but are designed to harness the kinetic energy of tidal currents. They are typically installed on the seafloor or on a foundation in areas with high tidal currents. As the tide flows, the blades of the turbine rotate, generating electricity. Tidal stream generators are a more recent development in tidal power technology and offer several advantages over tidal barrages, including lower costs and minimal environmental impact.
Tidal Lagoons
Tidal lagoons are a newer concept in tidal power technology. A tidal lagoon is a man-made structure that impounds a body of water, creating a reservoir of tidal energy. As the tide rises, water flows into the lagoon, creating a head of water. As the tide falls, the water is released back into the sea, passing through turbines, which generate electricity. Tidal lagoons offer several advantages over traditional tidal barrages, including lower costs and minimal environmental impact.
Benefits of Tidal Power
Tidal power offers several benefits, including predictability, reliability, and minimal environmental impact. Tidal currents are predictable, allowing for accurate forecasting of energy production. Tidal power is also reliable, as the tides are consistent and can be harnessed at any time. Additionally, tidal power has minimal environmental impact, as it does not emit greenhouse gases or other pollutants. Tidal power also has the potential to create jobs and stimulate local economies, particularly in coastal regions.
Cost of Tidal Power
The cost of tidal power is decreasing, making it more competitive with traditional forms of energy. The cost of tidal power is typically measured in terms of the levelized cost of energy (LCOE), which takes into account the cost of building and maintaining the tidal power facility, as well as the cost of generating electricity. The LCOE of tidal power is currently around $0.15-0.20 per kilowatt-hour, which is comparable to the cost of wind and solar power.
What is tidal power?
+Tidal power is a form of renewable energy that harnesses the natural power of ocean tides to generate electricity.
How does tidal power work?
+Tidal power works by harnessing the kinetic energy of ocean tides using various technologies, such as tidal barrages, tidal stream generators, and tidal lagoons.
What are the benefits of tidal power?
+Tidal power offers several benefits, including predictability, reliability, and minimal environmental impact. It also has the potential to create jobs and stimulate local economies, particularly in coastal regions.
In conclusion, tidal power is a promising form of renewable energy that has the potential to provide a significant portion of the world’s energy needs. With its predictability, reliability, and minimal environmental impact, tidal power is an attractive alternative to traditional forms of energy. As the cost of tidal power continues to decrease, it is likely to become a more viable option for countries around the world. By harnessing the power of the ocean’s tides, we can create a cleaner, more sustainable energy future for generations to come.