As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, environmental degradation, and energy security, the importance of adopting reusable energy sources has become increasingly evident. Reusable energy, also known as renewable energy, refers to the use of natural resources that can be replenished over time, such as sunlight, wind, and water. In this article, we will explore five ways reusable energy can help mitigate the negative impacts of fossil fuel consumption and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Key Points
- Solar energy can be harnessed using photovoltaic panels or solar thermal systems, providing a clean and abundant source of electricity.
- Wind energy can be generated using wind turbines, which convert the kinetic energy of wind into electrical power.
- Hydro energy, including tidal and wave power, can be harnessed using hydroelectric dams or ocean energy converters.
- Geothermal energy can be utilized to generate electricity or provide heating and cooling, leveraging the heat from the Earth's core.
- Bioenergy, derived from organic matter such as plants and waste, can be converted into electricity, heat, or transportation fuels.
Solar Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Sun

Solar energy is one of the most promising forms of reusable energy, with the potential to meet a significant portion of global electricity demand. Photovoltaic (PV) panels, which convert sunlight into electrical energy, have become increasingly efficient and cost-competitive with fossil fuels. Additionally, solar thermal systems can provide heat and hot water, reducing the need for conventional energy sources. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar energy could account for up to 27% of global electricity generation by 2050, making it a crucial component of a low-carbon energy mix.
Wind Energy: Tapping into the Power of the Wind
Wind energy is another vital source of reusable energy, with wind turbines generating electricity by converting the kinetic energy of wind into electrical power. Wind farms, both onshore and offshore, have become a common sight in many parts of the world, providing a clean and reliable source of energy. The Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC) estimates that wind power could meet up to 35% of global electricity demand by 2050, making it an essential contributor to a renewable energy future.
| Energy Source | Global Electricity Generation Potential by 2050 |
|---|---|
| Solar Energy | 27% |
| Wind Energy | 35% |
| Hydro Energy | 15% |
| Geothermal Energy | 5% |
| Bioenergy | 10% |

Hydro Energy: Harnessing the Power of Water
Hydro energy, including tidal and wave power, is a promising source of reusable energy, with the potential to provide a significant portion of global electricity demand. Hydroelectric dams, which harness the energy of moving water, have been a mainstay of renewable energy generation for decades. Additionally, ocean energy converters, such as tidal stream generators and wave energy converters, are being developed to tap into the vast energy potential of the world’s oceans. According to the IEA, hydro energy could account for up to 15% of global electricity generation by 2050.
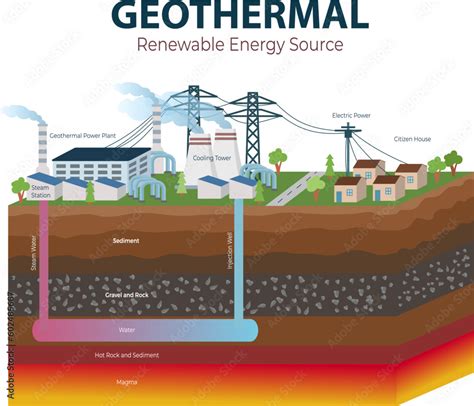
Geothermal Energy: Leveraging the Heat of the Earth
Geothermal energy, which harnesses the heat from the Earth’s core, is a vital source of reusable energy, with the potential to provide both electricity and heat. Geothermal power plants, which use hot water or steam from underground reservoirs to generate electricity, have been operating for decades. Additionally, geothermal heat pumps can provide space heating and cooling, reducing the need for conventional energy sources. The IEA estimates that geothermal energy could account for up to 5% of global electricity generation by 2050.
Bioenergy: Converting Organic Matter into Energy
Bioenergy, derived from organic matter such as plants and waste, is a promising source of reusable energy, with the potential to provide a significant portion of global energy demand. Bioenergy can be converted into electricity, heat, or transportation fuels, such as bioethanol and biodiesel. Additionally, bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) can remove more CO2 from the atmosphere than it emits, making it a vital component of a net-zero emissions future. According to the IEA, bioenergy could account for up to 10% of global energy demand by 2050.
What is the current status of reusable energy adoption worldwide?
+According to the IEA, renewable energy accounted for 26% of global electricity generation in 2020, with solar and wind energy being the fastest-growing sources. However, there is still a long way to go to meet global climate and energy goals, and increased investment and policy support are needed to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.
What are the main benefits of adopting reusable energy sources?
+The main benefits of adopting reusable energy sources include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving air quality, enhancing energy security, and creating jobs and stimulating local economies. Additionally, reusable energy sources can provide a reliable and consistent supply of energy, reducing the volatility of fossil fuel prices and enhancing energy independence.
What are the challenges associated with integrating reusable energy sources into the grid?
+The challenges associated with integrating reusable energy sources into the grid include ensuring a stable and efficient supply of electricity, managing the variability of renewable energy sources, and upgrading grid infrastructure to accommodate the integration of decentralized energy sources. Additionally, there may be issues related to energy storage, grid resilience, and cybersecurity that need to be addressed.
In conclusion, reusable energy sources offer a promising solution to the world’s energy and environmental challenges. By harnessing the power of the sun, wind, water, and heat from the Earth’s core, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, mitigate climate change, and create a more sustainable future. As the world continues to transition towards a low-carbon economy, it is essential that we prioritize the development and deployment of reusable energy technologies, and work towards a future where energy is clean, abundant, and accessible to all.



