As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, environmental degradation, and energy security, the importance of renewable energy has become increasingly evident. Renewable energy power types have emerged as a vital component of the global energy mix, offering a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. In this article, we will delve into the various types of renewable energy, exploring their characteristics, benefits, and potential applications.
Key Points
- Solar energy is one of the most widely available and accessible forms of renewable energy, with a global potential of 3.8 million exajoules per year.
- Wind energy is a significant contributor to the global renewable energy mix, with over 740 gigawatts of installed capacity worldwide.
- Hydrokinetic energy, including tidal and wave power, has the potential to generate up to 750 gigawatts of electricity globally.
- Geothermal energy can provide both heat and electricity, with an estimated global potential of 12.2 exajoules per year.
- Biomass energy, derived from organic matter, can be used for heat, electricity, and transportation, with a global potential of 270 exajoules per year.
Solar Energy
Solar energy is one of the most promising forms of renewable energy, harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity or heat. Photovoltaic (PV) systems and solar thermal systems are the two primary technologies used to capture solar energy. PV systems convert sunlight into electricity using semiconducting materials, while solar thermal systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight, generating heat that can be used for electricity generation or other applications. With a global potential of 3.8 million exajoules per year, solar energy is an attractive option for both residential and commercial use.
Solar Energy Applications
Solar energy has a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential installations to large-scale commercial and industrial projects. Solar-powered water pumps, solar cookers, and solar-powered buildings are just a few examples of the many innovative uses of solar energy. In addition, solar energy can be used for electricity generation, providing power to homes, businesses, and communities. The cost of solar energy has decreased dramatically in recent years, making it more competitive with fossil fuels and increasing its adoption worldwide.
| Renewable Energy Type | Global Potential |
|---|---|
| Solar Energy | 3.8 million exajoules per year |
| Wind Energy | 72 terawatts |
| Hydrokinetic Energy | 750 gigawatts |
| Geothermal Energy | 12.2 exajoules per year |
| Biomass Energy | 270 exajoules per year |
Wind Energy

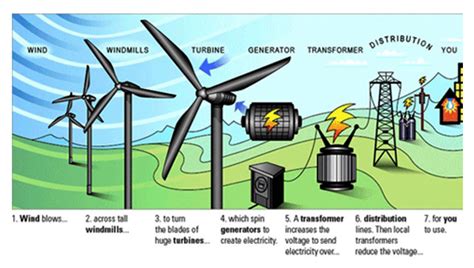
Wind energy is another significant contributor to the global renewable energy mix, with over 740 gigawatts of installed capacity worldwide. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electricity, using blades attached to a rotor to drive an electrical generator. Onshore and offshore wind farms are the two primary applications of wind energy, with offshore wind farms offering higher capacity factors and reduced visual impact. However, the intermittency of wind energy and the need for advanced energy storage technologies remain significant challenges to its widespread adoption.
Wind Energy Applications
Wind energy has a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential installations to large-scale commercial and industrial projects. Wind-powered water pumps, wind-powered generators, and wind-powered buildings are just a few examples of the many innovative uses of wind energy. In addition, wind energy can be used for electricity generation, providing power to homes, businesses, and communities. The cost of wind energy has decreased significantly in recent years, making it more competitive with fossil fuels and increasing its adoption worldwide.
Hydrokinetic Energy
Hydrokinetic energy, including tidal and wave power, has the potential to generate up to 750 gigawatts of electricity globally. Tidal power harnesses the energy of ocean tides, using barrages or tidal stream generators to convert the kinetic energy of the tides into electricity. Wave power, on the other hand, uses the energy of ocean waves to generate electricity, using a variety of technologies such as buoys, tidal stream generators, or oscillating water columns. However, the high cost of hydrokinetic energy technologies and the need for advanced materials and manufacturing processes remain significant challenges to its widespread adoption.
Hydrokinetic Energy Applications
Hydrokinetic energy has a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential installations to large-scale commercial and industrial projects. Tidal-powered water pumps, tidal-powered generators, and tidal-powered buildings are just a few examples of the many innovative uses of hydrokinetic energy. In addition, hydrokinetic energy can be used for electricity generation, providing power to homes, businesses, and communities. The potential of hydrokinetic energy to provide a reliable and constant source of renewable energy makes it an attractive option for the future.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy can provide both heat and electricity, using the natural heat of the Earth to generate power. Geothermal power plants use hot water or steam from underground reservoirs to drive a turbine, generating electricity. Geothermal energy has an estimated global potential of 12.2 exajoules per year, making it a significant contributor to the global renewable energy mix. However, the high cost of geothermal energy technologies and the need for advanced exploration and drilling techniques remain significant challenges to its widespread adoption.
Geothermal Energy Applications
Geothermal energy has a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential installations to large-scale commercial and industrial projects. Geothermal-powered heating systems, geothermal-powered cooling systems, and geothermal-powered buildings are just a few examples of the many innovative uses of geothermal energy. In addition, geothermal energy can be used for electricity generation, providing power to homes, businesses, and communities. The potential of geothermal energy to provide a reliable and constant source of renewable energy makes it an attractive option for the future.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy, derived from organic matter, can be used for heat, electricity, and transportation. Biomass power plants use a variety of feedstocks, including wood waste, agricultural waste, and energy crops, to generate electricity. Biomass energy has an estimated global potential of 270 exajoules per year, making it a significant contributor to the global renewable energy mix. However, the high cost of biomass energy technologies and the need for advanced feedstock production and logistics remain significant challenges to its widespread adoption.
Biomass Energy Applications
Biomass energy has a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential installations to large-scale commercial and industrial projects. Biomass-powered heating systems, biomass-powered cooling systems, and biomass-powered buildings are just a few examples of the many innovative uses of biomass energy. In addition, biomass energy can be used for electricity generation, providing power to homes, businesses, and communities. The potential of biomass energy to provide a reliable and constant source of renewable energy makes it an attractive option for the future.
What are the benefits of renewable energy?
+Renewable energy offers a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. Additionally, renewable energy can improve energy security, reduce energy costs, and create jobs and stimulate local economies.
What are the challenges of renewable energy?
+Renewable energy faces several challenges, including high upfront costs, intermittency, and energy storage limitations. Additionally, renewable energy technologies require advanced materials and manufacturing processes, and the need for grid infrastructure and energy storage solutions remains a significant challenge.
What is the future of renewable energy?
+The future of renewable energy is promising, with advancements in technology and decreases in cost making it more competitive with fossil fuels. As the world continues to transition towards a low-carbon economy, renewable energy is expected to play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
In conclusion, renewable energy power types offer a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. As the world continues to transition towards a low-carbon economy, renewable energy is expected to play a significant role in reducing energy costs, improving energy security, and creating jobs and stimulating local economies. While challenges remain, the benefits of renewable energy make it an attractive option for the future, and ongoing advancements in technology and decreases in cost are expected to drive its widespread adoption.