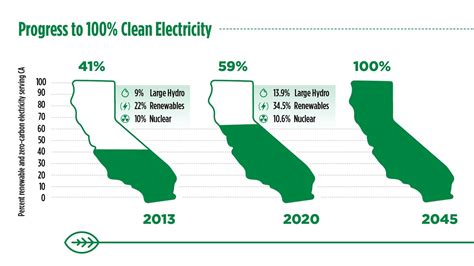
As the most populous state in the United States, California has been at the forefront of the renewable energy movement, driven by its ambitious climate goals and commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The state's renewable energy producers have played a crucial role in this transition, harnessing the power of solar, wind, and other clean energy sources to meet the growing demand for electricity. With a target of generating 60% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030, California's renewable energy sector is poised for significant growth, driven by innovative technologies, favorable policies, and increasing consumer demand.
The California renewable energy landscape is characterized by a diverse range of producers, from large utility-scale solar farms to smaller, community-based wind and geothermal projects. These producers have not only helped to reduce the state's reliance on fossil fuels but have also created new economic opportunities, generated jobs, and stimulated local economies. According to the California Energy Commission, the state's renewable energy industry has created over 100,000 jobs and generated $13.4 billion in economic benefits in 2020 alone. Furthermore, a study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory found that widespread adoption of renewable energy in California could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 78% by 2050, highlighting the critical role of renewable energy producers in achieving the state's climate goals.
Key Points
- California aims to generate 60% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030, with a focus on solar, wind, and geothermal energy.
- The state's renewable energy producers have created over 100,000 jobs and generated $13.4 billion in economic benefits in 2020, with a projected growth rate of 10% per annum.
- Renewable energy producers in California are driving innovation, with advances in technology, energy storage, and grid management, including the development of smart grids and virtual power plants.
- The state's renewable energy sector is expected to continue growing, driven by favorable policies, increasing consumer demand, and declining technology costs, with solar energy costs decreasing by 70% over the past decade.
- California's renewable energy producers are playing a critical role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, with a projected reduction of 78% by 2050, and are helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change, including droughts, wildfires, and sea-level rise.
Renewable Energy Sources in California

California’s renewable energy landscape is characterized by a diverse range of energy sources, each with its unique advantages and challenges. Solar energy, in particular, has emerged as a leading source of renewable energy in the state, with large-scale solar farms and rooftop solar installations generating a significant portion of the state’s electricity. According to the California Public Utilities Commission, solar energy accounted for 22.4% of the state’s electricity generation in 2020, up from 12.1% in 2018. Wind energy, on the other hand, has been a mainstay of California’s renewable energy sector, with wind farms in the Altamont Pass and Tehachapi Mountains generating electricity for decades. Geothermal energy, which harnesses the heat from the Earth’s core, is also an important contributor to the state’s renewable energy mix, with the Geysers geothermal field in Northern California being one of the largest in the world.
Solar Energy in California
Solar energy has experienced rapid growth in California, driven by declining technology costs, favorable policies, and increasing consumer demand. The state’s solar market is characterized by a mix of large-scale solar farms, community solar projects, and rooftop solar installations, with a total installed capacity of over 26,000 megawatts. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association, California has the largest solar market in the United States, with solar energy generating enough electricity to power over 7.5 million homes. The state’s solar industry has also created thousands of jobs, stimulated local economies, and generated significant economic benefits, with a projected growth rate of 15% per annum.
| Renewable Energy Source | Installed Capacity (MW) | Electricity Generation (GWh) |
|---|---|---|
| Solar | 26,000 | 43,600 |
| Wind | 5,500 | 13,400 |
| Geothermal | 2,700 | 12,300 |
| Hydro | 14,000 | 23,100 |
Challenges and Opportunities for Renewable Energy Producers
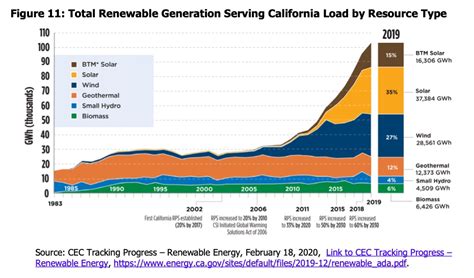
Despite the growth and success of California’s renewable energy sector, producers face a range of challenges and opportunities that will shape the future of the industry. One of the primary challenges is the intermittency of renewable energy sources, which can make it difficult to ensure a stable and reliable supply of electricity. Energy storage technologies, such as batteries, have emerged as a critical solution to this challenge, enabling producers to store excess energy generated during periods of high production and release it during periods of high demand. According to a report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, the cost of energy storage has decreased by 70% over the past decade, making it more feasible for renewable energy producers to adopt this technology.
Energy Storage and Grid Management
Energy storage and grid management are critical components of a reliable and efficient renewable energy system. California’s grid operators, such as the California Independent System Operator (CAISO), are working to integrate renewable energy sources into the grid, while also ensuring that the grid remains stable and reliable. Advanced technologies, such as smart grids and virtual power plants, are being developed to manage the flow of energy and optimize the performance of renewable energy systems. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, the widespread adoption of smart grids could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 45% by 2030, highlighting the critical role of energy storage and grid management in achieving California’s climate goals.
In conclusion, California's renewable energy producers are playing a critical role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change. As the state continues to transition towards a low-carbon economy, the renewable energy sector is expected to continue growing, driven by innovative technologies, favorable policies, and increasing consumer demand. However, the industry must also address challenges related to energy storage, grid management, and land use, requiring a nuanced understanding of the complex interdependencies between technology, policy, and market forces.
What is the current status of renewable energy in California?
+California has made significant progress in renewable energy, with solar energy accounting for 22.4% of the state’s electricity generation in 2020. The state aims to generate 60% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030, with a focus on solar, wind, and geothermal energy.
What are the challenges facing renewable energy producers in California?
+Renewable energy producers in California face a range of challenges, including the intermittency of renewable energy sources, energy storage, and grid management. However, advances in technology, declining costs, and increasing consumer demand are driving growth and innovation in the sector.
What role do energy storage and grid management play in California’s renewable energy sector?
+Energy storage and grid management are critical components of a reliable and efficient renewable energy system. Advanced technologies, such as smart grids and virtual power plants, are being developed to manage the flow of energy and optimize the performance of renewable energy systems.