The debate between energy cells and power cells has been a longstanding one, with each having its own set of advantages and disadvantages. In the realm of energy storage, these two types of cells are often compared and contrasted, with the terms sometimes being used interchangeably. However, it is essential to understand the subtle differences between them to appreciate their unique characteristics and applications. In this article, we will delve into the world of energy cells and power cells, exploring their definitions, functionalities, and the scenarios in which one might be preferred over the other.
Understanding Energy Cells

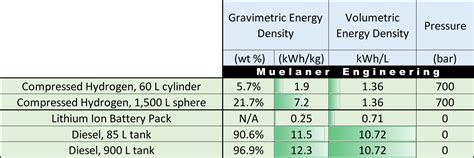
Energy cells, also known as batteries, are designed to store energy over a prolonged period. They are characterized by their high energy density, which enables them to provide a sustained flow of energy to devices and systems. Energy cells are typically used in applications where a steady supply of power is required, such as in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. The energy density of a cell is measured in watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg), which indicates the amount of energy stored per unit of mass. Energy cells with high energy density are preferred in applications where weight and volume are critical factors.
Types of Energy Cells
There are several types of energy cells, including lithium-ion (Li-ion), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and lead-acid batteries. Li-ion batteries are widely used in portable electronics due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and relatively low self-discharge rate. NiMH batteries, on the other hand, are commonly used in hybrid and electric vehicles, while lead-acid batteries are often used in automotive and industrial applications. Each type of energy cell has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of cell depends on the specific requirements of the application.
| Energy Cell Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion (Li-ion) | 100-265 | 300-1000 cycles |
| Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) | 60-120 | 300-1000 cycles |
| Lead-acid | 35-40 | 200-300 cycles |

Understanding Power Cells

Power cells, on the other hand, are designed to provide high power output over a short period. They are characterized by their high power density, which enables them to deliver a large amount of power in a short time. Power cells are typically used in applications where high power pulses are required, such as in power tools, electric motors, and renewable energy systems. The power density of a cell is measured in watts per kilogram (W/kg), which indicates the amount of power delivered per unit of mass. Power cells with high power density are preferred in applications where high power output is required.
Types of Power Cells
There are several types of power cells, including ultracapacitors, lithium-ion capacitors, and fuel cells. Ultracapacitors, also known as supercapacitors, are designed to store electrical energy through electrostatic double-layer capacitance and electrochemical pseudocapacitance. They offer high power density, long cycle life, and rapid charging and discharging capabilities. Lithium-ion capacitors, on the other hand, combine the benefits of lithium-ion batteries and ultracapacitors, offering high energy density and high power density. Fuel cells, such as proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells, offer high power density and high efficiency, making them suitable for applications where high power output is required.
| Power Cell Type | Power Density (W/kg) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Ultracapacitor | 1000-10000 | 1-10 |
| Lithium-ion capacitor | 100-1000 | 10-100 |
| Fuel cell (PEM) | 1000-5000 | 100-1000 |
Key Points
- Energy cells are designed to store energy over a prolonged period, while power cells are designed to provide high power output over a short period.
- Energy cells have high energy density, while power cells have high power density.
- The choice of energy cell or power cell depends on the specific requirements of the application.
- Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in portable electronics, while ultracapacitors are used in power tools and electric motors.
- Fuel cells offer high power density and high efficiency, making them suitable for applications where high power output is required.
In conclusion, energy cells and power cells are both essential components in modern energy systems. While energy cells are designed to store energy over a prolonged period, power cells are designed to provide high power output over a short period. The choice of energy cell or power cell depends on the specific requirements of the application, including energy density, power density, and cost. By understanding the characteristics and applications of energy cells and power cells, we can design and develop more efficient and effective energy systems.
What is the main difference between energy cells and power cells?
+The main difference between energy cells and power cells is their design purpose. Energy cells are designed to store energy over a prolonged period, while power cells are designed to provide high power output over a short period.
What are the applications of energy cells and power cells?
+Energy cells are used in applications such as consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems, while power cells are used in applications such as power tools, electric motors, and renewable energy systems.
What is the advantage of using lithium-ion batteries?
+Lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density, long cycle life, and relatively low self-discharge rate, making them suitable for applications such as portable electronics and electric vehicles.
Meta description: Learn about the difference between energy cells and power cells, including their characteristics, applications, and advantages. Discover how to choose the right type of cell for your specific needs. (147 characters)