Wind power energy has emerged as a significant contributor to the global renewable energy landscape, offering a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, energy security, and environmental degradation, the importance of harnessing wind energy cannot be overstated. With advancements in technology and infrastructure, the applications of wind power energy have expanded beyond electricity generation, encompassing a wide range of uses that cater to diverse economic, social, and environmental needs.
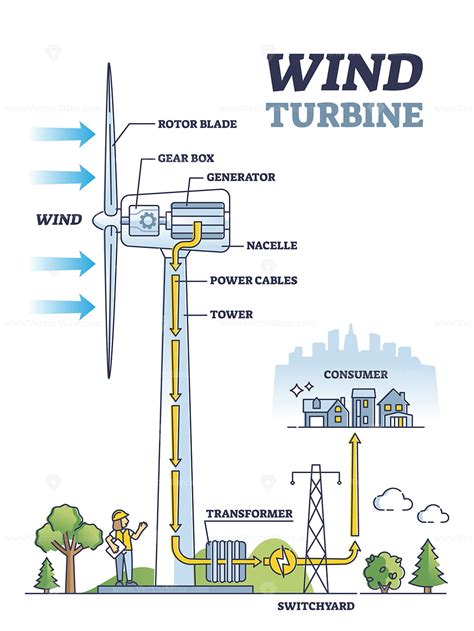
The fundamental principle behind wind power energy is the conversion of kinetic energy from wind into electrical or mechanical energy. This is achieved through the use of wind turbines, which are designed to capture the wind's kinetic energy and convert it into a usable form. The versatility of wind power energy lies in its potential to serve both as a primary source of energy and as a complementary component of hybrid energy systems, integrating with other renewable energy sources like solar, hydro, and geothermal power to create resilient and efficient energy grids.
Key Points
- Wind power energy is a renewable, sustainable, and environmentally friendly source of energy.
- It can be used for electricity generation, water pumping, and other mechanical applications.
- Wind energy contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change impacts.
- Technological advancements have improved the efficiency and affordability of wind energy systems.
- Wind power can be integrated into hybrid energy systems for enhanced energy security and reliability.
Applications of Wind Power Energy
One of the most prominent applications of wind power energy is in the generation of electricity. Wind farms, consisting of multiple wind turbines, are installed in areas with high wind speeds to maximize energy production. The electricity generated can be fed into the grid, powering homes, industries, and public facilities. This application not only helps in reducing dependence on fossil fuels but also contributes to lowering carbon emissions, thereby playing a crucial role in global efforts to combat climate change.
Water Pumping and Irrigation
Beyond electricity generation, wind power energy is also utilized for water pumping and irrigation purposes, particularly in rural and agricultural areas. Wind-powered water pumps offer a reliable and cost-effective means of accessing water for drinking, agriculture, and livestock, especially in regions where access to conventional energy sources is limited. This application is particularly significant in developing countries, where it can enhance food security, improve livelihoods, and support sustainable agricultural practices.
In addition to these applications, wind power energy is increasingly being explored for its potential in hydrogen production, desalination, and even in the propulsion of ships and vehicles. The versatility of wind energy stems from its ability to be adapted and integrated into various energy systems and applications, making it a vital component of the transition towards a more sustainable and renewable energy future.
| Wind Power Application | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Electricity Generation | Conversion of wind energy into electricity | Reduces greenhouse gas emissions, enhances energy security |
| Water Pumping and Irrigation | Use of wind energy for pumping water | Supports agriculture, enhances food security, and provides access to clean water |
| Hydrogen Production | Production of hydrogen using wind energy | Promotes the development of clean transportation, reduces dependence on fossil fuels |

Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the numerous benefits and applications of wind power energy, there are challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential. These include issues related to intermittency, where the unpredictability of wind speeds can affect energy production, and concerns over the visual and environmental impacts of large-scale wind farms. Moreover, the high upfront costs of installing wind energy infrastructure, although decreasing over time, can be a barrier to adoption in some regions.
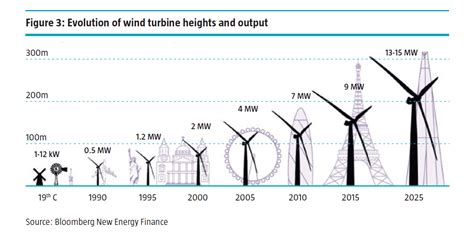
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth. Advances in wind turbine technology, such as larger, more efficient blades and advanced materials, are improving the cost competitiveness of wind energy. Furthermore, the development of floating wind turbines and other innovative designs is opening up new areas for wind farm development, including deeper waters and more complex terrains, thereby expanding the global potential for wind power generation.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
A supportive policy and regulatory framework is crucial for the development and integration of wind power energy into national and international energy systems. Governments and regulatory bodies can play a pivotal role by implementing policies that encourage investment in wind energy, such as tax incentives, feed-in tariffs, and net metering laws. Additionally, setting ambitious renewable energy targets and enforcing strict environmental standards can help drive the transition towards a more sustainable energy mix.
Public awareness and education are also vital components in the widespread adoption of wind power energy. By highlighting the benefits, addressing misconceptions, and engaging local communities in the planning and development process, it is possible to build support and foster a sense of ownership and participation in wind energy projects. This not only helps in reducing resistance to new developments but also ensures that the benefits of wind power are equitably distributed and aligned with local needs and priorities.
What are the primary benefits of wind power energy?
+The primary benefits of wind power energy include its renewable and sustainable nature, contribution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and enhancement of energy security by diversifying the energy mix.
How does wind power energy contribute to climate change mitigation?
+Wind power energy contributes to climate change mitigation by reducing dependence on fossil fuels, thereby lowering carbon emissions. Each unit of electricity generated from wind power displaces a unit that would have been produced from burning fossil fuels, leading to a net reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
What are some of the challenges facing the widespread adoption of wind power energy?
+Challenges facing the widespread adoption of wind power energy include intermittency, high upfront costs, and concerns over visual and environmental impacts. However, technological innovations, policy support, and public engagement are helping to address these challenges and make wind power more viable and acceptable.
In conclusion, wind power energy represents a critical component of the global transition towards a more sustainable, renewable, and environmentally friendly energy future. Its applications are diverse, ranging from electricity generation and water pumping to emerging uses in hydrogen production and transportation. While challenges exist, the opportunities for growth, innovation, and policy support are substantial, underscoring the potential for wind power energy to play a leading role in shaping the energy landscape of the future.



